Match the description of the murmur to the valvular lesion – Matching the description of a murmur to the corresponding valvular lesion is a fundamental skill in cardiovascular medicine. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the characteristics of murmurs, the common valvular lesions associated with them, and the mechanisms by which these lesions produce murmurs.
By understanding the relationship between murmurs and valvular lesions, clinicians can accurately diagnose and manage valvular heart disease.
The identification of murmurs involves assessing their timing, location, and intensity using auscultation and phonocardiography. Valvular lesions, such as stenosis and regurgitation, produce characteristic murmurs due to abnormal blood flow patterns across the affected valve.
Matching Murmurs to Valvular Lesions
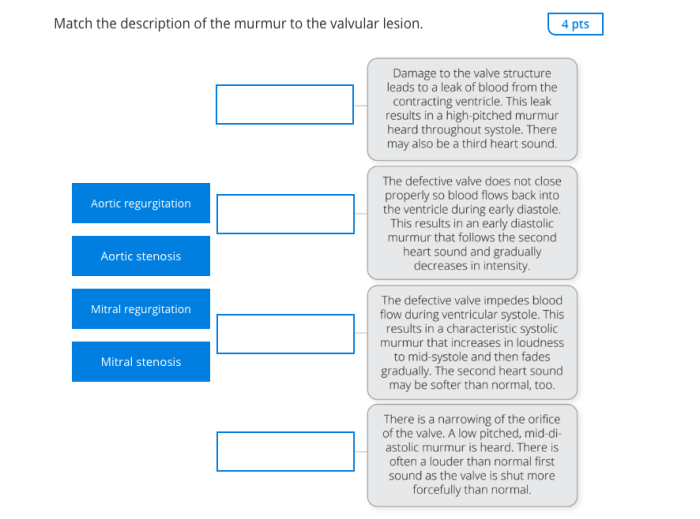
The presence of a murmur on auscultation of the heart can indicate an underlying valvular lesion. Matching the characteristics of the murmur to the corresponding valvular lesion is essential for accurate diagnosis and management.
Identifying the Murmur
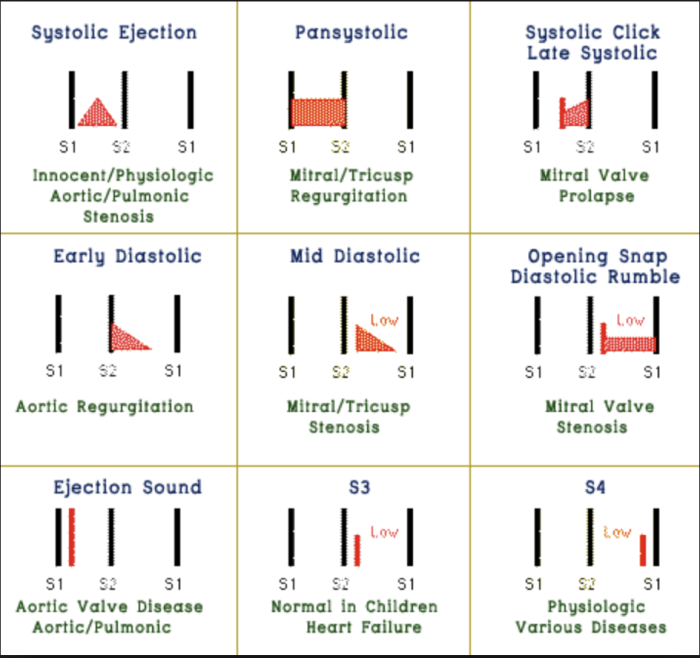
Murmurs are abnormal heart sounds that can be detected by auscultation using a stethoscope. They are characterized by their timing, location, and intensity.
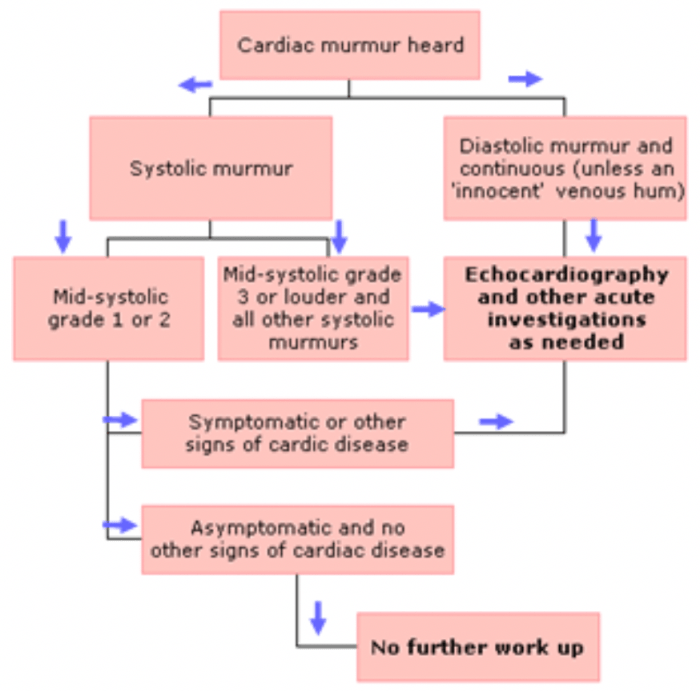
Timing: Murmurs can occur during systole (the contraction of the ventricles), diastole (the relaxation of the ventricles), or both.
Location: Murmurs can be heard at different locations on the chest, such as the apex, base, or along the left or right sternal border.
Intensity: Murmurs are graded on a scale of 1 to 6, with 1 being the faintest and 6 being the loudest.
Auscultation and phonocardiography are two techniques used to identify murmurs. Auscultation involves listening to the heart sounds directly with a stethoscope, while phonocardiography is a technique that records and amplifies heart sounds for further analysis.
Determining the Valvular Lesion
Common valvular lesions associated with murmurs include:
- Mitral regurgitation
- Mitral stenosis
- Aortic regurgitation
- Aortic stenosis
- Tricuspid regurgitation
- Pulmonary stenosis
Valvular lesions can produce murmurs through various mechanisms, such as abnormal blood flow through a narrowed or leaking valve.
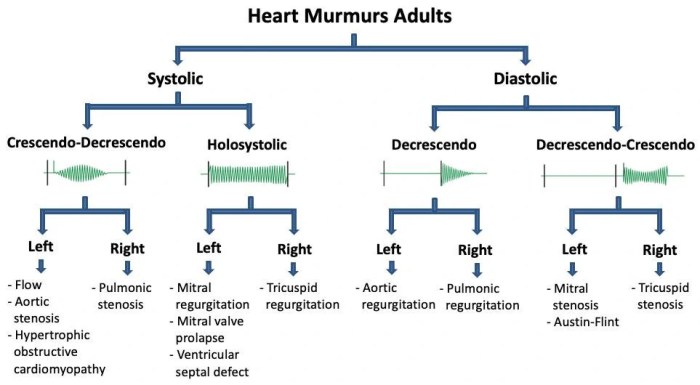
Matching the Murmur to the Lesion
| Murmur Characteristics | Valvular Lesion | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Holosystolic, blowing murmur at the apex | Mitral regurgitation | Pan-systolic murmur |
| Mid-diastolic, rumbling murmur at the apex | Mitral stenosis | Mid-diastolic rumble |
| Diastolic, blowing murmur at the aortic base | Aortic regurgitation | Early diastolic murmur |
| Systolic, crescendo-decrescendo murmur at the aortic base | Aortic stenosis | Ejection systolic murmur |
| Holosystolic, blowing murmur at the lower left sternal border | Tricuspid regurgitation | Pan-systolic murmur |
| Systolic, ejection murmur at the upper left sternal border | Pulmonary stenosis | Ejection systolic murmur |
Differential Diagnosis
Other conditions that can produce similar murmurs to valvular lesions include:
- Innocent murmurs (common in children and adolescents)
- Hyperthyroidism
- Anemia
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Cardiac shunts
Differentiating between murmurs caused by valvular lesions and other conditions requires careful clinical assessment, including physical examination, electrocardiography, and echocardiography.
Clinical Implications, Match the description of the murmur to the valvular lesion
Matching murmurs to valvular lesions is clinically significant because it allows for:
- Early detection and diagnosis of valvular lesions
- Assessment of the severity of valvular lesions
- Guidance for appropriate medical or surgical treatment
- Monitoring of disease progression
Questions and Answers: Match The Description Of The Murmur To The Valvular Lesion
What are the key characteristics of murmurs?
Murmurs are abnormal heart sounds characterized by their timing, location, and intensity. Timing refers to when the murmur occurs in the cardiac cycle, location indicates where it is best heard on the chest, and intensity describes its loudness.
How are valvular lesions associated with murmurs?
Valvular lesions, such as stenosis and regurgitation, disrupt normal blood flow across the heart valves. These abnormal flow patterns create vibrations that produce murmurs.
What is the importance of matching murmurs to valvular lesions?
Matching murmurs to valvular lesions allows clinicians to identify the underlying cause of the murmur and determine the severity of the valvular lesion. This information guides appropriate management strategies and improves patient outcomes.