Select all the true statements concerning prokaryotic organisms – Prokaryotic organisms, the oldest and most abundant life forms on Earth, hold immense significance in various fields. Select All True Statements Concerning Prokaryotic Organisms delves into the fascinating world of these microorganisms, exploring their defining characteristics, diverse roles, and applications.
From their unique cellular structure to their ecological impact and medical relevance, this article provides a comprehensive overview of prokaryotes, shedding light on their profound influence on our planet and our lives.
Characteristics of Prokaryotic Organisms: Select All The True Statements Concerning Prokaryotic Organisms
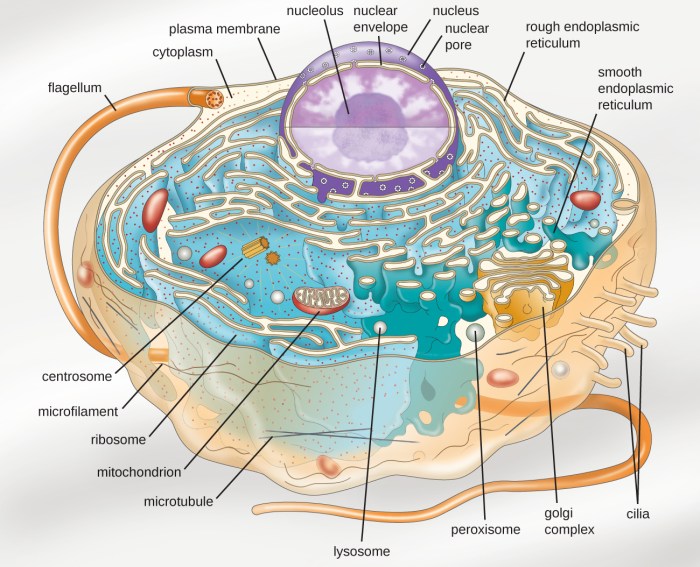
Prokaryotic organisms are the simplest and most abundant form of life on Earth. They are characterized by their lack of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Instead, the genetic material of prokaryotes is contained in a single, circular chromosome located in the cytoplasm.
Prokaryotes are also distinguished from eukaryotes by their cell wall, which is made up of peptidoglycan. The cell wall helps to protect the cell from its surroundings and gives it shape.
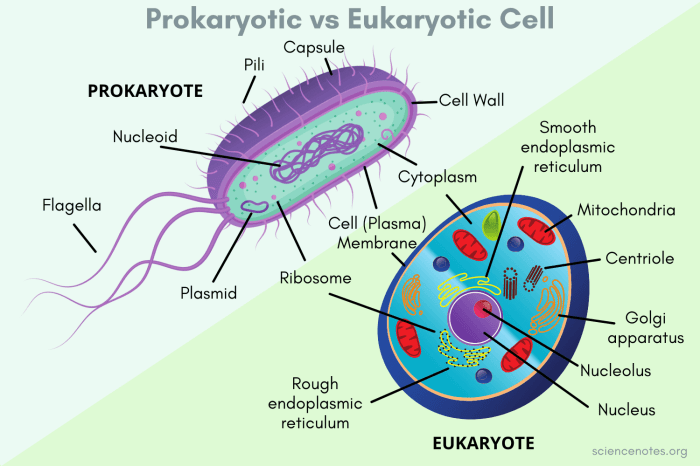
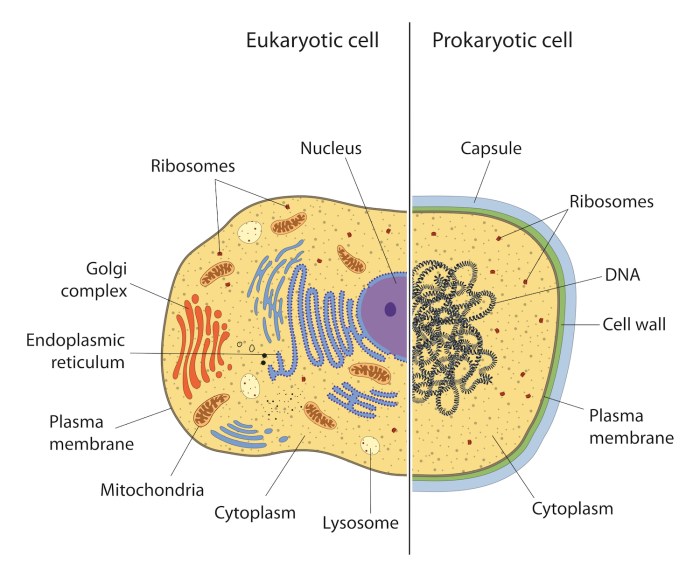
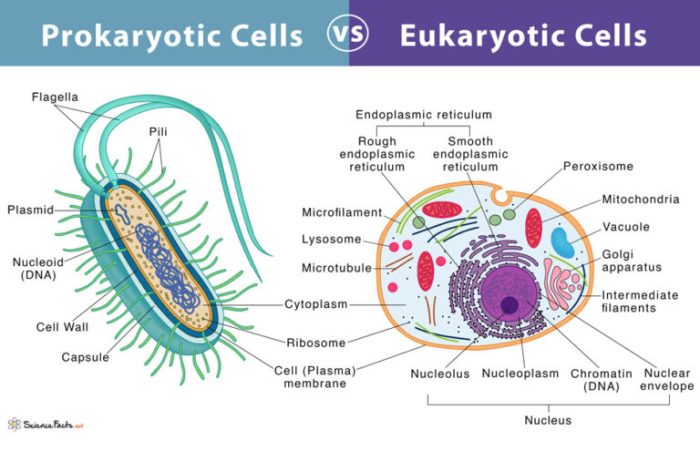
Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
- Prokaryotic cells have a single, circular chromosome located in the cytoplasm.
- Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall made up of peptidoglycan.
- Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells have multiple, linear chromosomes located in the nucleus.
- Eukaryotic cells do not have a cell wall.
Significance of the Cell Wall
The cell wall is an important part of the prokaryotic cell. It helps to protect the cell from its surroundings and gives it shape. The cell wall also helps to regulate the movement of materials into and out of the cell.
Reproduction in Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes reproduce by binary fission, a process in which the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Binary fission is a simple and efficient way to reproduce, and it allows prokaryotes to rapidly increase their population size.
In addition to binary fission, prokaryotes can also exchange genetic material through a process called horizontal gene transfer. Horizontal gene transfer can occur through conjugation, transduction, or transformation.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer is an important mechanism for genetic diversity in prokaryotes. It allows prokaryotes to acquire new genes from other organisms, which can help them to adapt to new environments.
Plasmids, Select all the true statements concerning prokaryotic organisms
Plasmids are small, circular pieces of DNA that are found in many prokaryotes. Plasmids are not essential for cell survival, but they can confer a variety of benefits to the cell, such as antibiotic resistance or the ability to metabolize new compounds.
Diversity of Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are a diverse group of organisms that can be found in a wide variety of habitats. Some prokaryotes are free-living, while others are parasites or symbionts.
| Morphology | Habitat | Metabolic Capabilities | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cocci | Soil, water, human body | Aerobic, anaerobic | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae |
| Bacilli | Soil, water, human body | Aerobic, anaerobic | Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis |
| Spirilla | Water, soil | Aerobic, anaerobic | Vibrio cholerae, Treponema pallidum |
| Archaea | Extreme environments (e.g., hot springs, deep sea) | Aerobic, anaerobic | Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum, Halobacterium salinarum |
Prokaryotes play an important role in the cycling of nutrients in the environment. They are also used in a variety of industrial and medical applications.
Prokaryotes and Disease
Some prokaryotes are pathogens, which means that they can cause disease in humans and other animals. Pathogenic prokaryotes include bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Bacteria are the most common type of pathogenic prokaryote. They can cause a wide range of diseases, including pneumonia, meningitis, and food poisoning.
Viruses are not technically prokaryotes, but they are often classified as such because they share some of the same characteristics. Viruses are parasites that can only reproduce inside the cells of other organisms. Viruses can cause a variety of diseases, including the common cold, influenza, and AIDS.
Fungi are a diverse group of organisms that include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. Some fungi are pathogenic and can cause diseases such as athlete’s foot, ringworm, and histoplasmosis.
Applications of Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are used in a variety of industrial and medical applications. For example, bacteria are used to produce antibiotics, enzymes, and other useful compounds.
Prokaryotes are also used in environmental applications, such as bioremediation. Bioremediation is the use of microorganisms to clean up contaminated environments.
FAQ
What are the key characteristics of prokaryotic organisms?
Prokaryotic organisms are characterized by their lack of a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles, a single circular chromosome, and a cell wall made of peptidoglycan.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Prokaryotes reproduce asexually through binary fission, where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
What is the significance of horizontal gene transfer in prokaryotes?
Horizontal gene transfer allows prokaryotes to exchange genetic material with other bacteria, promoting genetic diversity and adaptation.
What are the different groups of prokaryotes based on their morphology?
Prokaryotes can be classified into three main groups based on their morphology: spherical (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), and spiral (spirilla).
What are the applications of prokaryotes in biotechnology?
Prokaryotes are used in the production of antibiotics, enzymes, and other valuable compounds. They also play a role in bioremediation and environmental applications.